Module 1 Exercises
- What characteristics could be added to those listed in Section 1.2 for (a) good metalanguage design, (b) good documentation, (c) good functionality, and (d) good outputs?
- Consider a language of copy statements. Both the left-hand side and the right-hand side contain identifiers. The following is a "program" in this language:
- Finish the parse tree and corroborate the attribute values for the parse tree of Example 6
- What are three possible functions of the optimization process?
- Create all templates as in Example 7 to output code for the two assignment statements.
- Modify the regular expression for an identifier to include $ and _ (underscore) after the leading letter.
- Using the set of productions shown in Example 3, show that:
- Match each of the following compiler functions with the phase that performs it.
- Identify some tokens in your favorite computer language. Create your own names for the types. For example, if your language has arithmatic operators, say, +, -, *, /, you might have a type called ArithOp with these four values or you might identify two types MulOp with values * and / and AddOp with values + and -.
- Show the results after each of the six phases for a program consisting of the single
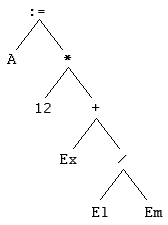
- What is the assignment statement represented by the following abstract syntax tree?
- Following the model of the IF Statement whose abstract syntax tree is shown in Section 1.6.2, create an
- For each of the following, give another term or word with the same meaning:
- Bootsrapping: Suppose we want to create a compiler for (a) a new language on a machine that has compilers for
Save := A; A := B; B := Save;(a) Show the input to a lexical analyzer generator
(b) Show the output from the generated lexical analyzer
(c) Show the input to a parser generator
(d) Show the output from the resulting parser
y := z + 1 - x + 5
is a statement.
| (a) | Assigns a variable to register 5 | (i) | Lexical Analysis |
| (b) | Identifies loop as a label | (ii) | Syntax Analysis |
| (c) | Changes A + 4 * 3 to A + 12 | (iii) | Semantic Analysis |
| (d) | Finds a variable that has not been declared | (iv) | Optimization |
| (e) | Changes A := A + 12 to Add #12, A | (v) | Preparatioin for Code Generation |
| (f) | Creates a parse tree | (vi) | Code Generation |
Solution
assignment statement: Max := Min + 4 * 3 ;
Solution
abstract syntax tree for:
(a) If A < B THEN Min := A Else Min := B
(b) While Count < 100 DO Count := Count + 1
(a) Token
(b) Syntax analysis
(c) Parse Tree
(d) Intermediate representation
(e) Abstract syntax tree
(f) Analysis phases
(g) Synthesis phases
other languages or (b) a new machine for a language for which a compiler on another machine. Consider each case
separately:
(a) Language L is new to machine M. Language L has no compiler.
There is, however, a compiler for language Y
on machine M. One can create a
compiler for L in two steps:
Step 1: Using language
Y, write a compiler that translates (compiles) a small subset L0 of
language L
to the assembly language of machine M.
Step 2: Using the subset
L0, write a compiler that translates all of L to the machine
language of M.
Show how to use these programs to create a compiler that is written in the assemmbly language of M and compiles L programs to the assembly language of M.
(b) Machine N is brand new. There are no compilers for any
languages. However, there is a compiler for language
L(written in L0 ,
a subset of L) on machine M. A compiler for L can be created for
machine N in two steps:
Step 1: Change the code
generator of the compiler on M so that it puts out code for machine N rather
than M.
Step 2: Run the whole new
compiler through the old compiler. That is, compile the soure for
the compiler with
the new code generator and compile it using the L compiler as a program
on M putting out M assembly
language. Then we have a (cross) compiler on M, written in M that
converts L programs to N's assembly
language.
Show how to use these two steps to create a compiler for L written in the assembly language of N that translates to the assembly language of N, i.e., a compiler for L on machine N.
- Solution