Assigned: Tuesday, 27th Nov. 2001
Due: Tuesday, 4th Dec. 2001
Maximum: 100pts.
Purpose of homework: To become familiar with file organizations, indexes,
sorting and query processing.
NOTES: This homework is to be done by an individual student, no team work
allowed.
Consider a relation stored as a randomly ordered file for which the only index is an unclustered index on a field called sal.
Problem 2: [ 25 pts ]
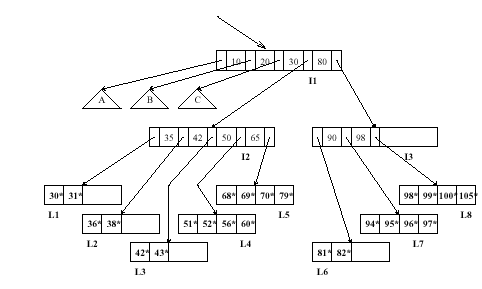
Consider the B+ tree index shown in the following figure, which uses Alternative (1) for data entries. Each intermediate node can hold up to five pointers and four key values. Each leaf can hold up to four records, and leaf nodes are doubly linked as usual, although these links are not shown in the figure (refer to textbook Fig. 9.29.)

Answer the following questions.
Problem 3: [ 20 pts ]
Assume that you have just built a dense B+ tree index using Alternative (2) on a heap file containing 20,000 records. The key field for this B+ tree index is a 40-byte string, and it is a candidate key. Pointers (i.e., record ids and page ids) are (at most) 10-byte values. The size of one disk page is 1,000 bytes. The index was built in a bottom-up fashion using the bulk-loading algorithm, and the nodes at each level were filled up as much as possible.
Answer the following questions.
Problem 4: [ 20 pts ]
Suppose that you have a file with 10,000 pages and that you have five buffer pages. Answer the following questions for each of these scenarios, assuming that our most general external sorting algorithm is used:
Problem 5: [ 20 pts ]
Consider the join R![]() R.a=S.bS,
given the following information about the relations to be joined.
R.a=S.bS,
given the following information about the relations to be joined.
- Relation R contains 10,000 tuples and has 10 tuples per page.
- Relation S contains 2,000 tuples and also has 10 tuples per page.
- Attribute b of relation S is the primary key for S.
- Both relations are stored as simple heap files. Neither relation has any indexes built on it.
- 52 buffer pages are available.
The cost metric is the number of page I/Os unless otherwise noted, and the cost of writing out the result should be uniformly ignored.
Answer the following questions.