CS 4514 Computer Networks
WPI, C Term 1995
Craig E. Wills
Midterm Exam (100 pts)
Given: Friday, Feb 3, 1995
NAME:
BOX:
1.5em
1.5em
This is a closed book (and notes) examination. Answer all questions
on the exam itself. Take the number of points assigned to each problem
and the amount of space provided for your answer as a measure of the
length and difficulty of the expected solution. The exam totals 100
points.
Potentially useful formulas:
- Nyquist rule for a noiseless channel:
max data rate = 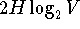 bps where H is the bandwidth and V
is the number of states encoded.
bps where H is the bandwidth and V
is the number of states encoded. - Shannon's theorem for channels with noise:
max data rate = 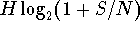 where noise is measured in decibels
(db) and
where noise is measured in decibels
(db) and
db = 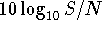
SCORE:
- (4 points) Which type of transport service did the original USENET
network use: circuit switching, message switching or packet switching?
- (6 points)
What baud rate is required to realize a 10 Mbps data rate using Manchester
encoding? Using differential Manchester encoding?
- (10 points)
What is the Hamming distance for the following set of four 6-bit codewords?
000000 000111 111000 111111
- How many single-bit errors can be guaranteed to be detected
for this set?
- How many single-bit errors can be guaranteed to be corrected
for this set?
- (18 points) This question concerns the use of CRC checksums, which you
implemented in the first assignment.
- Assume that a new CRC polynomial ``CEW-3'' polynomial
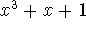 is
defined. How many bits will the resulting checksum contain?
is
defined. How many bits will the resulting checksum contain?
- Calculate the checksum if the data being sent is the character `a'
(hexadecimal 61).
- What will be the bit string that is actually transmitted?
- What is the remainder when this bit string is divided by the
CEW-3 polynomial?
-
Are there any other bit strings of this length that yield the same
remainder when divided by CEW-3? If so, indicate one. If not, briefly
explain why no others exist.
- (10 points)
What is the maximum data rate that can be achieved over a 3 kHz voice grade
line with a signal-to-noise ratio of 30 dB? What is the maximum data rate
if 3 bits of data are encoded for each baud on this line?
- (10 points)
Station A has two frames in a queue ready to send. Station B has one frame
ready to send at the same time. On an 802.3 CSMA/CD network, is it
guaranteed that Station B's frame will be transmitted before the second
frame of Station A is transmitted? Why? What is the answer for the same
scenario on an 802.5 token ring network? Assume all frames have the same
priority.
- (10 points)
The following diagram shows the bottom three layers of the OSI
reference model on two separate machines. Name these three layers.
What is the path of communication when sending data from layer 3 on machine
A to layer 3 on machine B? As part of your answer indicate any
headers/trailers that are added to/removed from the data.
- (10 points)
Define in-band signaling and out-of-band signaling in the
context of data communication and give an example where each is used.
- (15 points)
Suppose two stations are using CSMA/CD with a modified version of the
binary exponential backoff algorithm. In the modified algorithm, each
station will always wait 0 or 1 time slots regardless of how many
collisions have occurred. Assume two stations have just sent
transmissions that have collided.
- What is the probability that contention ends on the first round of
retransmissions?
- What is the probability that contention ends on the second round of
retransmissions?
- What is the probability that contention ends on the third round of
retransmissions?
- In general how does this algorithm compare with the normal
binary exponential backoff algorithm in terms of performance under
different types of load?
- (7 points)
If the minimum packet size for the 802.3 LAN standard is 64 bytes and the
data rate of the network is 10 Mbps then what does this indicate about
 , the propagation delay, for such a network?
, the propagation delay, for such a network?