 |
| 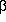
Step One: Direct-Recursion
For each rule which contains a left-recursive option,
 |
| 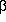
introduce a new nonterminal A' and rewrite the rule as
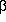 A'
A'  |
|  A'
A'
Thus the production:
is left-recursive with "E" playing the role of "A","+ T" playing the role of
 , and "T" playing the role of
, and "T" playing the role of
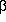 A'.
Introducing the new nonterminal E', the
production can be replaced by:
A'.
Introducing the new nonterminal E', the
production can be replaced by:
 | + T E'
| + T E'
Of course, there may be more than one left-recursive part on the right-hand side. The general rule is to replace:

 |
| 
 | ...
| ...
 |
| 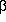
 |
| 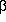
 | ... |
| ... | 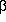

by
A --> 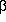
 A' |
A' |
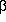
 A'|
...|
A'|
...|
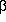
 A'
A'
A' -->  |
| 
 A'
|
A'
| 
 A'
| ...|
A'
| ...| 
 A'
A'
Note that this may change the "structure". For the expression above, the original grammar is left-associative, while the non-left recursive one is now right-associative.
Step one describes a rule to eliminate direct left recursion from a production. To eliminate left-recursion from an entire grammar may be more difficult because of indirect left-recursion. For example,
B --> C D
C --> A | c
D --> d
is indirectly recursive because
A --> B x y | x
A ==> B x y ==> C D x y ==> A D x y.
A ==> ... ==> A 
where  is
is D x y. The algorithm eliminates left-recursion entirely. It contains a "call" to a procedure which eliminates direct left-recursion (as described in step one).
Example 3 illustrates this algorithm for the grammar of Example 3.
