Due: Tuesday, May 2nd, 11:59pm
Total points: 23
Homework will be turned in online (canvas) in written form, saved as a PDF.
(1 point) The sampling distribution of the mean can always be approximated by the normal distribution (select all that apply).
(1 point) For samples of N=3 (i.e., there are 3 observations in the sample), the sampling distribution of the mean (i.e., the distribution of the mean values if multiple samples are taken) will be normally distributed (check all that apply):
(1 point) If a particular set of data is normally distributed, you would find that approximately (check all that apply):
(1 point) The size (magnitude) of a confidence interval depends upon (check all that apply):
(1 point) Which of the following is true (check all that apply):
(1 point) As a WPI admissions intern, you are tasked with estimating the number of admitted students (class of '26) that will be IMGD majors. You sample 300 admitted students to WPI and find that 45 of them are planning on being IMGD majors. The 95% confidence interval for the fraction of incoming students planning on being IMGD majors is 0.15 +- 0.04. Interpret this interval.
(1 point) In Hypothesis testing, the Null Hypothesis (H0) is:
(1 point) In hypothesis testing, the p value is (pick the answer that matches best):
(1 point) In simple linear regression, the y-intercept (b) represents the:
(1 point) In simple linear regression, the slope (m) represents the:
(1 point) A simple linear regression model for predicting a player's points (Y) is 6 X + 10, where X is the player's level. How many more points can a level 10 player expect to get when they level up to level 11?
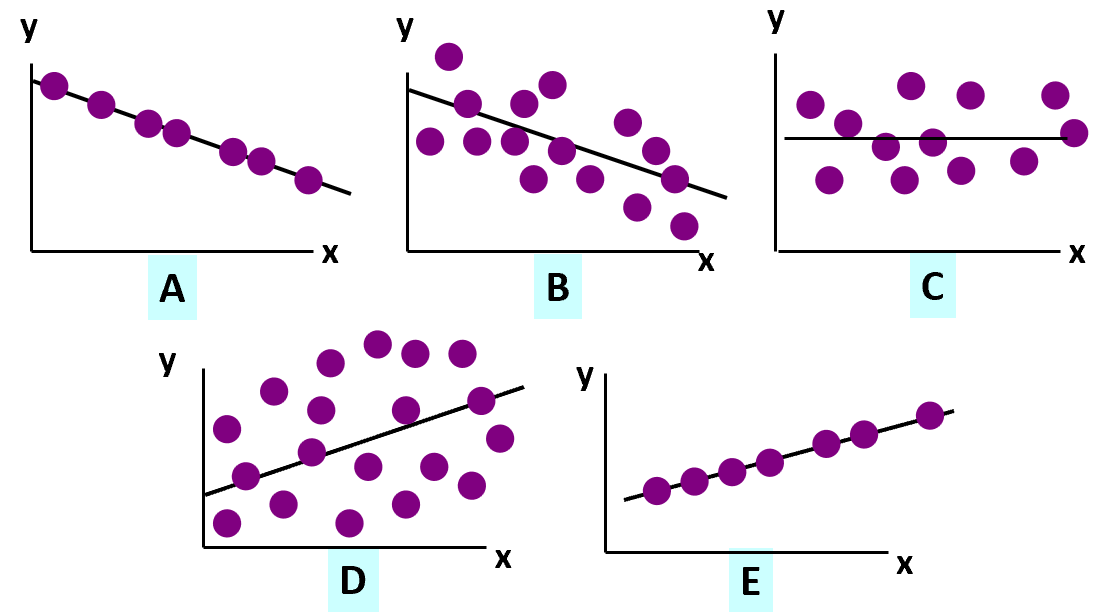
(1 point) Match the scatter plots A-E that best match each of the following correlations: 0, -1, 0.3, -0.6, and 1.0.

(1 point) The strength of the relationship between two numerical variables is measured by the:
(1 point) The residuals represent:
(1 point) The regression sum of squares (SSR) can never be greater than the total sum of squares (SST).
(1 point) The value of R (the correlation) is always positive.
(1 point) The coefficient of determination (R2) is a measurement of how much variability in Y is explained by it's relationship (model) to X.
(1 point) Considering extrapolation and interpolation as discussed in class, which answer fits best:
$72.95 Instacart
$85.13 Amazon Fresh
$85.85 Fresh Direct
$92.13 Shipt
$72.70 Thrive Market
$82.19 Hungry Hippo
$72.57 Peapod(4 points) You built a racing game, Goat Runner, where players ride goats around alumni track.
You sample the time around the track for 30 players and find the mean is about 15.71 seconds with a standard deviation of 4.63 seconds. Find a 90% confidence interval for the population mean time round this track.
You decide the game is too easy, and add a few hurdles the goats have to jump over. A sample of another 30 players shows the mean time around the track is now 18.90 seconds with a standard deviation of of 7.1 seconds. Find a 90% confidence interval for the population mean time round this track.
Draw a column chart with data from #a and #b, depicting the 90% confidence interval.
Interpret the chart, including using the confidence intervals, in your comparisons of the two tracks.
 Return to the IMGD 2905 home page
Return to the IMGD 2905 home page